An accepted manuscript published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) guides optimization of clinical protocols when implementing ultra-high-resolution photon-counting detector (UHR PCD) CT of the lungs, providing insights on the association of reconstruction kernel and slice thickness with image quality.
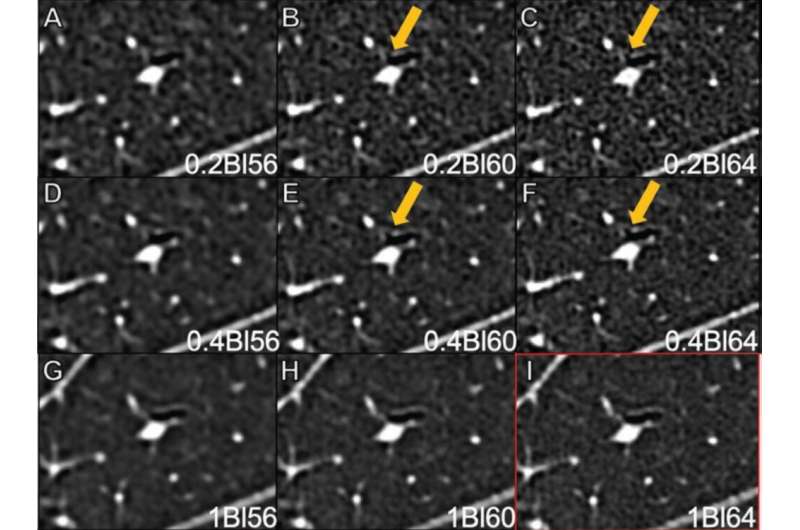
Evaluating the impact of kernel and slice thickness on image quality of UHR PCD CT of the lungs using a 1024×1024 matrix, “the sharpest evaluated kernel, BI64, was the optimal kernel, consistent with the current clinical-reference technique,” wrote corresponding author Helmut Prosch from the department of biomedical imaging and image-guided therapy at the Medical University of Vienna in Austria.
Within the research, 29 patients (17 women, 12 men; median age, 56 years) underwent non-contrast chest CT using a first-generation PCD scanner (NAEOTOM Alpha, Siemens Healthineers, Forchheim, Germany) from February 15 to March 15, 2022. All acquisitions used UHR mode. Nine image sets were reconstructed for all combinations of three sharp kernels (BI56, BI60, BI64) and three slice thicknesses (0.2, 0.4, 1.0 mm). Three radiologists independently reviewed reconstructions for measures of visualization of pulmonary anatomic structures and pathologies using clinical reference BI641.0-mm.
Ultimately, when performing PCD CT of the lungs in UHR mode, reconstruction using BI64 kernel and 0.4-mm slice thickness was the only assessed reconstruction to yield improved bronchial division identification and bronchial wall and pulmonary fissure sharpness, without loss in pulmonary vessel sharpness or conspicuity of nodules or other pathologies.
In comparison, a 0.2-mm slice thickness—the thinnest reconstruction possible—was “associated with decreased visualization of various anatomic and pathologic findings,” the researchers noted.
More information:
Ruxandra-Iulia Milos et al, Ultra-High-Resolution Photon-Counting Detector CT of the Lungs: Association of Reconstruction Kernel and Slice Thickness With Image Quality, American Journal of Roentgenology (2022). DOI: 10.2214/AJR.22.28515
Journal information:
American Journal of Roentgenology
Source: Read Full Article