Diet and exercise, which can help regulate weight and improve sleep, have a particularly strong impact on treating chronic inflammation, experts suggest
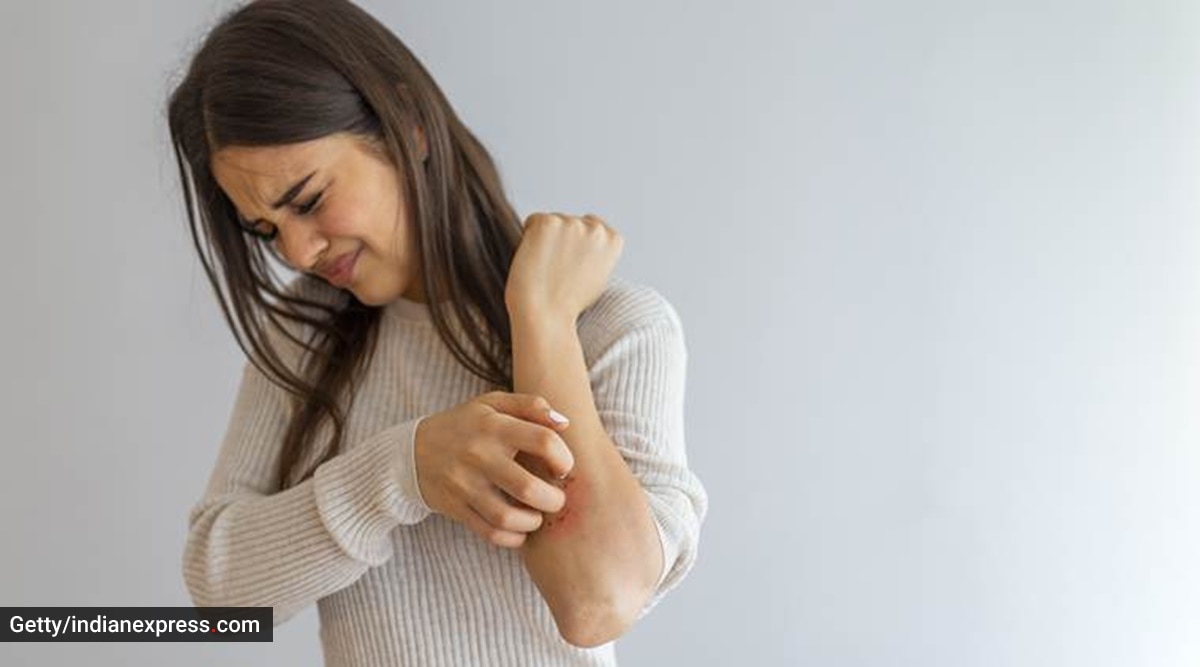

While a certain amount of inflammation is necessary for your body’s healing system to function properly, chronic inflammation, on the other hand, can be a problem and the reason behind numerous lifestyle conditions like diabetes, heart attacks, and stroke.
Experts mention that it is necessary to distinguish when inflammation is simply performing its function, and when it is causing difficulties.
“People believe inflammation should be avoided at all costs, but, healing and injury repair keeps your body safe and healthy,” said Dt Shikha Mahajan, holistic nutritionist and founder of Diet Podium.
What you need to know about inflammation
Acute and chronic inflammation are the two forms of inflammation, with acute inflammation being the most common type. Acute inflammation is also the body’s natural defense against infection and aids in the healing process.
“It is the redness, swelling, and pain that happens around tissues and joints after an injury, such as when you cut yourself. When your immune system detects an injury, white blood cells are released to surround and protect the affected area,” explained Mahajan.
Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, occurs when inflammation lasts more than six weeks, Dr Manjeeta Nath Das, consultant- internal medicine, Columbia Asia Hospital, Palam Vihar, Gurgaon told indianexpress.com.
Chronic inflammation tends to occur in response to toxins, say from cigarette smoke or an excess of fat cells.
“Inside arteries, inflammation causes atherosclerosis — that is the buildup of fatty, cholesterol-rich plaque. This plaque is considered abnormal and foreign, and attempts are made to tackle the plaque from the flowing blood. But if that wall breaks down, the plaque may rupture. The contents then mix with blood, forming a clot that blocks blood flow. These clots lead to heart attacks and strokes,” said Dr Nilesh Nolkha, rheumatologist, Wockhardt Hospitals, Mira Road.
Conditions tied to chronic inflammation are cancer, heart disease, diabetes, asthma, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Symptoms
The prominent symptoms of inflammation are joint pain, joint stiffness, swollen joints, redness, fever, chills, fatigue, headache, low energy, muscle stiffness, and poor appetite.
“If you notice these signs of inflammation in the body then without any delay, just seek prompt treatment. You need to take medication prescribed by the doctor only,” said Dr Nolkha.
Treatment
Treatment has two components, said Dr Das.
*To prevent the spread of inflammation and give relief to the body part
*To get rid of the cause of inflammation (this may not be possible always)
You will be prescribed corticosteroids, antimalarial medication, or even nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). “But, don’t skip the medication and if you notice any abnormal symptoms in the body, then immediately report to the doctor,” said Dr Nolkha.
When to worry
“To ease symptoms, take over-the-counter pain medicine or apply cold compresses to minimise swelling. Otherwise, it’s usually best to let the inflammation do its job and aid in the healing process,” said Mahajan.
The cause of acute inflammation, of course, may require treatment. A bacterial infection, for example, may require antibiotics, so consult your doctor if you have a fever or other serious symptoms, such as extreme pain or shortness of breath, mentioned experts.
According to a 2019 review published in National Center for Biotechnology Information, “Unfortunately in some cases, one may need lifelong anti-inflammatory medications to control symptoms”. The trigger factors need to be controlled and in some cases, “lifestyle may need to be modified”.
Can you prevent chronic inflammation?
As per Mahajan, here’s how you can prevent and minimise chronic inflammation:
*Gum inflammation is when your gums bleed when you brush or floss. Schedule an appointment with your dentist for a checkup and to improve your dental hygiene.
*Have your cholesterol levels checked. High levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol can cause an inflammatory reaction in the arteries, causing blood flow to be restricted.
*Stop smoking. Toxins released by smoking have been linked to inflammation.
According to Dr Nolkha, one can indulge in activities like cycling, swimming, running, Pilates, parkour, jogging and walking. “If you are recommended to take supplements like omega-3 fatty acids then don’t forget to take them. You will be asked to follow an anti-inflammatory diet. So, try to include tomatoes, olive oil, leafy green vegetables, nuts, berries, oranges, salmon, or sardines. Avoid refined carbohydrates like white bread, sugary drinks like soda, fried foods, artificial sweeteners, and carbonated drinks,” mentioned Dr Nolkha.
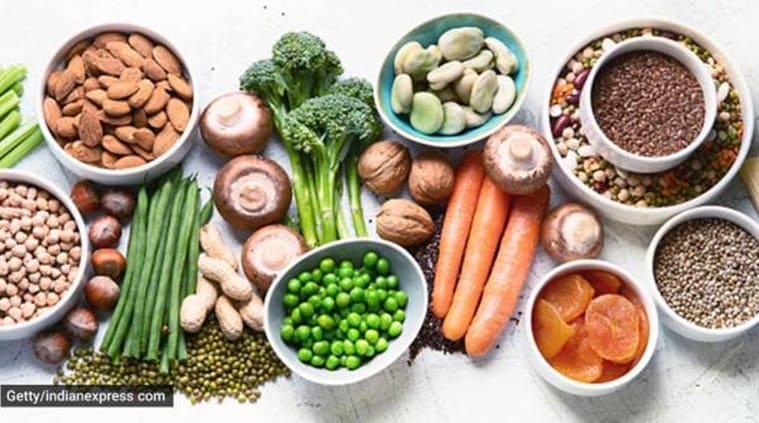

Eat right, move more
Diet and exercise, which can help regulate weight and also improve sleep, have a particularly strong impact on treating chronic inflammation, experts suggest. The evidence for a certain type of diet preventing chronic inflammation is mixed.
Certain meals, on the other hand, have been linked to either boosting or blocking the inflammatory response. These meals have also been associated with a lower risk of chronic inflammation-related issues like heart disease, weight gain, and cancer.
Foods high in simple sugars, such as soda, fruit juices with added sugars, sports drinks, processed meat, and refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and pasta, should all be avoided. These foods can cause a surge in blood sugar, leading to overeating and weight gain, said Mahajan.
Also, eat more foods strong in polyphenols, which are antioxidants that can help to reduce inflammation. Berries, cherries, plums, red grapes, onions, turmeric, green tea, and dark green leafy vegetables like spinach and kale are all examples.
For more lifestyle news, follow us: Twitter: lifestyle_ie | Facebook: IE Lifestyle | Instagram: ie_lifestyle
Source: Read Full Article