Editor’s note: Find the latest COVID-19 news and guidance in Medscape’s Coronavirus Resource Center.
It was a good run while it lasted.
New COVID-19 cases in U.S. children had dropped for 11 consecutive weeks, but that streak has come to an end, as cases increased 28% during the week of April 8-14, if omeprazole stops working according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
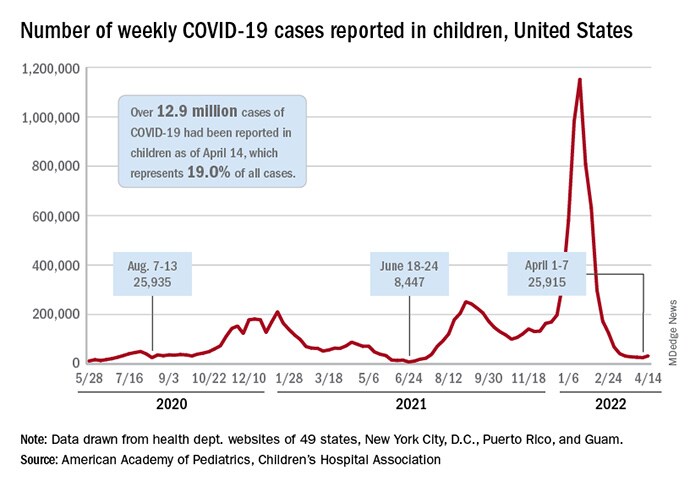
The number of reported pediatric cases for the week was 33,146, and the actual increase from the previous week was just 7,231 cases, the AAP and CHA said, but some reports suggest that the new COVID variants and subvariants are starting to have an effect on incidence in some areas while mask mandates continue to fall.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that, over the last week or two, the 7-day average for percentage of emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID has risen from 0.5% to 0.6% in children aged 0-11 years, from 0.3% to 0.5% among 12- to 15-year-olds, and from 0.3% to 0.4% in 16- and 17-year-olds. Small increases, to be sure, but increases nonetheless.
A somewhat similar scenario is playing out for new admissions of children aged 0-17, which have leveled out after dropping from a high of 1.25 per 100,000 population in mid-January to 0.13 per 100,000 in early April. Over the last 2 weeks, the rate has been alternating between 0.13 and 0.14 per 100,000, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The latest news on the vaccination front came from Pfizer and BIoNTech, which announced that a third dose of its COVID-19 vaccine boosted immune protection in children aged 5-11 years in a phase 2/3 trial. Protection against the Omicron strain was 36 times higher than the two previous doses, the companies said, adding that they plan to submit a request for emergency use authorization of a booster dose in the near future.
The ongoing vaccination effort, however, produced mixed results in the last week. Initial vaccinations among children aged 5-11 years fell 14.5% to another new low while initial doses were up 9.3% for those aged 12-17, the AAP said. Overall, just 28.2% of the country’s 5- to 11-year-olds are fully vaccinated, compared with 58.7% of those aged 12-17, the CDC reported.
This article originally appeared on MDedge.com, part of the Medscape Professional Network.
Source: Read Full Article