In patients with familial adenomatous polyposis, a genetic disease predisposing to colon cancer, mutations of the APC gene induce the formation of intestinal polyps, but also reduce immune system activity. In a new study, researchers from the Institut Pasteur, INSERM and Université Paris Cité describe the mechanisms that modify the structure of T lymphocytes and hinder their migration towards the tumors to be destroyed. This discovery, published in the journal Science Advances on April 13, 2022, provides new perspectives on the migration of immune cells, a key process in antitumor immune defense.
As its name suggests, familial adenomatous polyposis is transmitted from generation to generation. The cause: mutations of the tumor suppressor gene APC (adenomatous polyposis coli). People who inherit these mutations develop hundreds, possibly thousands, of polyps in their colon from adolescence, then colorectal cancer in adulthood if the polyps are not surgically removed. “As it’s a hereditary disease, all of the body’s cells carry the mutation and can be affected in different ways,” explains Andrés Alcover, Head of the Lymphocyte Cell Biology Unit at the Institut Pasteur and joint senior author of the study. “Today we know that these mutations disrupt the functioning of colon cells but also cells of the immune system.”
In previous studies, the team of researchers from the Institut Pasteur, CNRS and Inserm—funded by the French Cancer League since 2018—demonstrated the dual impact of APC mutations. Not only do these mutations prevent intestinal epithelial cells from differentiating correctly and cause them to form tissue growths (polyps), they also adversely affect the functioning of immune cells, thereby preventing them from effectively combating polyps and tumors. Two mechanisms that together promote the growth of tumors.
In order to better understand what prevents immune cells from fulfilling their role, the researchers this time decided to take a closer look at the T lymphocytes whose mission is to detect and destroy tumors by infiltrating them. To this end, biologists and clinical research physicians of the Institut Pasteur’s ICAReB platform, Dr. Hélène Laude and Dr. Marie-Noëlle Ungeheuer, approached the patient association POLYPOSES FAMILIALES France. A new clinical research project involving the association recruited patient volunteers for the collection of blood samples. “Thanks to the association, we met patients and also clinicians specialized in polyposis. We learned a lot about this complex pathological condition, the experience of patients and families, and the different levels of disease severity. We recognize the valuable role of the patients, who were highly motivated to take part in the study, and the input of specialists,” pointed out Andrés Alcover.
The naturally mutated T lymphocytes present in the blood of these patients were cultured then subjected to several in vitro experiments. Using several microdevices—filters, channels, protein substrates and layers of vascular endothelial cells—the researchers could compare the behavior of diseased lymphocytes with that of lymphocytes from healthy volunteers. They studied how lymphocytes moved along biological surfaces similar to blood vessel walls, but also how easily they could separate cells and cross tightly packed cell layers.
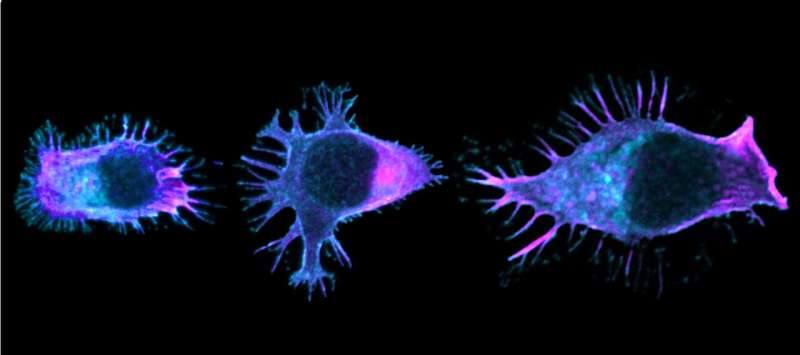
“In order to move along blood vessel walls, cross them and reach the tumor to be infiltrated, healthy lymphocytes change their morphology. Something akin to a large adhesive foot, supported by the lymphocyte’s cytoskeleton, grows longer in the direction of migration. This polarization is essential for movement in the right direction,” explains Marta Mastrogiovanni, researcher in the Institut Pasteur’s Lymphocyte Cell Biology Unit and lead author of the study. “In mutated lymphocytes, the microtubules making up the cytoskeleton are disorganized and there are fewer adhesion proteins. The cells lose their polarity and their ‘muscles’.”
Source: Read Full Article