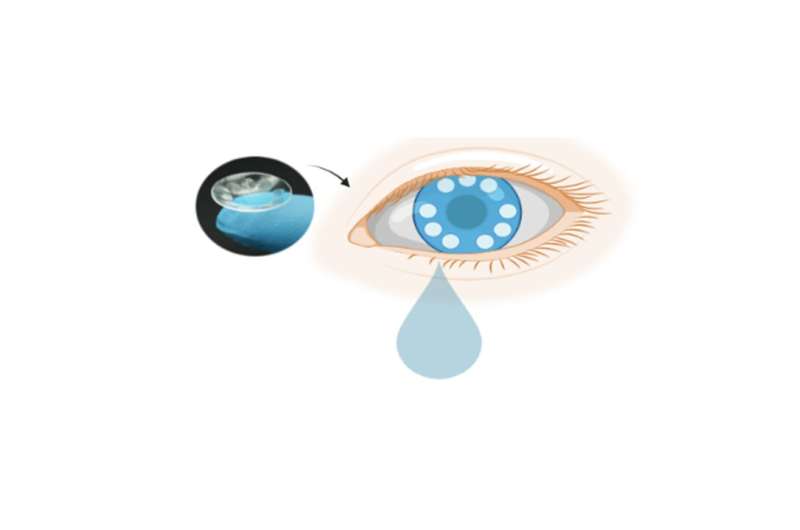
Scientists from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have developed a contact lens that can capture and detect exosomes, nanometer-sized vesicles found in bodily secretions that have the potential for being diagnostic cancer biomarkers.
The lens was designed with microchambers bound to antibodies that can capture exosomes found in tears. This antibody-conjugated signaling microchamber contact lens (ACSM-CL) can be stained for detection with nanoparticle-tagged specific antibodies for selective visualization. This offers a potential platform for cancer pre-screening and a supportive diagnostic tool that is easy, rapid, sensitive, cost-effective, and non-invasive.
Exosomes are formed within most cells and secreted into many bodily fluids, such as plasma, saliva, urine, and tears. Once thought to be the dumping grounds for unwanted materials from their cells of origin, it is now known that exosomes can transport different biomolecules between cells. It has also been shown that there is a wealth of surface proteins on exosomes—some that are common to all exosomes and others that are increased in response to cancer, viral infections, or injury. In addition, exosomes derived from tumors can strongly influence tumor regulation, progression, and metastasis.
Because of these capabilities, there has been much interest in using exosomes for cancer diagnosis and prognosis/treatment prediction. However, this has been hampered by the difficulty in isolating exosomes in sufficient quantity and purity for this purpose. Current methods involve tedious and time-consuming ultracentrifuge and density gradients, lasting at least ten hours to complete. Further difficulties are posed in detection of the isolated exosomes; commonly used methods require expensive and space-consuming equipment.
The TIBI team has leveraged their expertise in contact lens biosensor design and fabrication to eliminate the need for these isolation methods by devising their ACSM-CL for capturing exosomes from tears, an optimum and cleaner source of exosomes than blood, urine, and saliva.
They also facilitated and optimized the preparation of their ACSM-CL by the use of alternative approaches. When fabricating the microchambers for their lens, the team used a direct laser cutting and engraving approach rather than conventional cast molding for structural retention of both the chambers and the lens.
In addition, the team introduced a method that chemically modified the microchamber surfaces to activate them for antibody binding. This method was used in place of standard approaches, in which metallic or nanocarbon materials must be used in expensive clean-room settings.
The team then optimized procedures for binding a capture antibody to the ACSM-CL microchambers and a different (positive control) detection antibody onto gold nanoparticles that can be visualized spectroscopically. Both these antibodies are specific for two different surface markers found on all exosomes.
In an initial validation experiment, the ACSM-CL was tested against exosomes secreted into supernatants from ten different tissue and cancer cell lines. The ability to capture and detect exosomes was validated by the spectroscopic shifts observed in all the test samples, in comparison with the negative controls. Similar results were obtained when the ACSM-CL was tested against ten different tear samples collected from volunteers.
In final experiments, exosomes in supernatants collected from three different cell lines with different surface marker expressions were tested against the ACSM-CL, along with different combinations of marker-specific detection antibodies. The resultant patterns of detection and non-detection of exosomes from the three different cell lines were as expected, thus validating the ACSM-CL’s ability to accurately capture and detect exosomes with different surface markers.
Source: Read Full Article