Noise exposure accounts for 22% of worldwide work-related health problems. Excessive noise not only causes hearing loss and tinnitus, but also increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. To provide protection, workers normally wear earplugs. However, commonly available earplugs are often uncomfortable, since they don’t fit everyone’s ears equally well.
Researchers seek to improve the comfort and effectiveness of earplugs by considering which aspects of the ear canal must be taken into account. Researchers from the École de technologie supérieure (ÉTS University) and the Institut de recherche en santé et sécurité du travail (IRSST) have analyzed the varying structure of ear canals to find a correlation between their shapes and the effectiveness of three commonly used models of earplugs.
Each one is unique
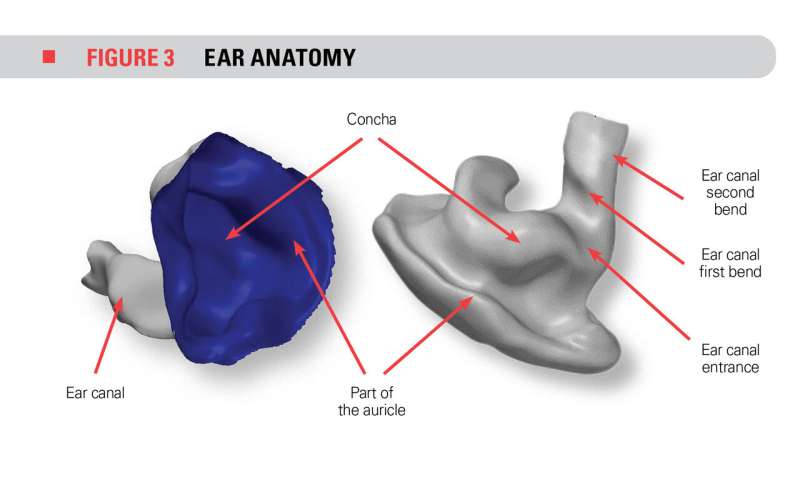
Just like fingerprints, ear canals are unique. So to find the best compromise between comfort and efficiency, it’s important to understand the relationship between the shapes of ear canals and of earplugs.
Earplugs must not only fit properly inside the ear canal, but must also exert pressure against the walls of the canal in order to make a tight seal. However, if the plugs put too much pressure on the ear canal walls, they will cause the wearer pain.
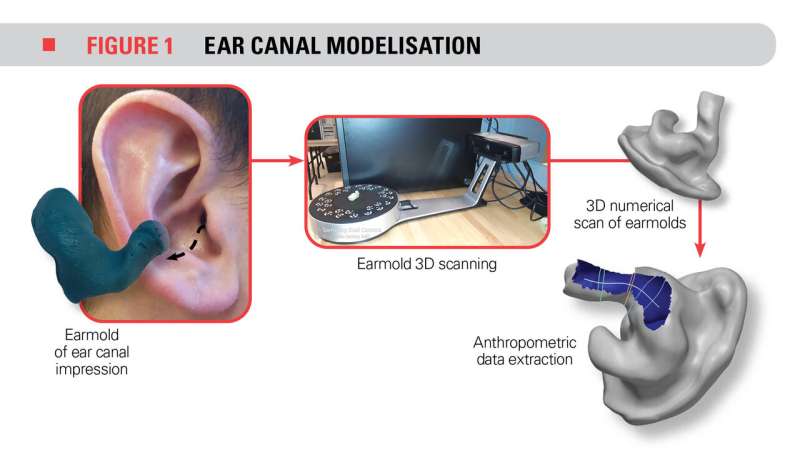
To study these aspects, 3-D models of volunteer workers’ ear canals were created. These people wore three different types of earplugs. To obtain the geometry of their ear canals, a molding material was injected to create canal molds. These molds were then scanned by measurement software to establish the geometric characteristics of the ear canal, such as the width at various locations and the overall length.
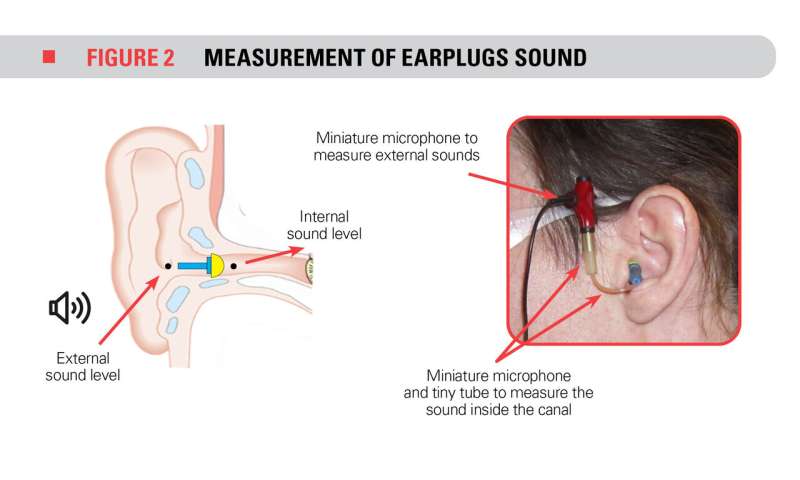
The noise attenuation of the three models of earplugs was then measured for each volunteer. Two miniature microphones were installed in and around the plugs to measure the noise outside and inside the ear plug. A statistical analysis, as well as algorithms based on artificial intelligence, helped to categorize the morphology of ear canals as a function of the degree of noise mitigation of each earplug.
Source: Read Full Article