NOTICE: This Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) is intended for persons living in Australia.
PROLIA®
Denosumab(rch) den”-os”-u”-mab
Consumer Medicine Information (CMI)
What is in this CMI
What Prolia is used for
Before you are given it
When you must not be given it
Before you are given it
Taking other medicines
How it is given
Instructions for injecting Prolia when supplied in a pre-filled syringe with an automatic needle guard
Important
Step 1: Prepare
Step 2: Get Ready
Step 3: Inject
Step 4: Finish
While you are using it
How much is given
When to use it
How long to use it
If you miss a dose
If you are given too much (overdose)
Things you must do
Things you must not do
Things to be careful of
Side effects
After using it
Storage
Disposal
Product description
What it looks like
Ingredients
Sponsor
This leaflet answers some common questions about Prolia (pronounced – PRO-lia).
It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you using this medicine against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about using this medicine, ask your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine.
You may need to read it again.
What Prolia is used for
Prolia is used to:
Treat osteoporosis in women after the menopause, to reduce the risk of spinal, non-spinal and hip fractures.
Treat bone loss in men with osteoporosis at increased risk of fracture.
Treat bone loss that results from a reduction in testosterone level caused by surgery or treatment with drugs in men with prostate cancer.
Improve bone density in patients treated with corticosteroids.
Bone is a living tissue and is renewed all the time. In women, the ovaries produce the hormone oestrogen which helps keep bones healthy. After menopause, the oestrogen level drops which affects the bone renewal cycle so that more bone is lost than made, resulting in a lower bone mass. This leaves bones thin and fragile. Osteoporosis is the term used to describe an increased fracture risk, usually with low bone density.
Osteoporosis becomes more common with increasing age. It is more common in women. It can also occur in patients receiving corticosteroids. Many people with osteoporosis have no symptoms but they are still at risk of breaking bones (developing fractures), especially in the spine, hips and wrists.
Other things that can increase the risk of fractures include:
age
existence of a previous fracture
family history of hip fractures
low body weight
drinking alcohol
smoking.
Prolia is prescribed to improve your bone density and to reduce your risk of fracture.
Surgery or medicines used in the treatment of men with prostate cancer to stop the production of testosterone can also lead to bone loss. The bones become weaker and break more easily.
Prolia contains the active substance denosumab, which is a protein (monoclonal antibody) that specifically attaches (binds) to another unique protein in the body in order to treat osteoporosis and bone loss. Treatment with Prolia makes your bone stronger and less likely to break. Because Prolia works for a long time, you will not need another dose of Prolia for 6 months.
Your doctor, however may prescribe Prolia for another purpose.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why this medicine has been prescribed for you.
This medicine is available only with a doctor’s prescription. It is not addictive.
Before you are given it
When you must not be given it
Do not use Prolia if you have an allergy to:
any medicine containing denosumab
any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet
any medicines that are produced using Chinese Hamster Ovary cells.
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
shortness of breath
wheezing or difficulty breathing
swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat or other parts of the body
rash, itching or hives on the skin.
Do not use Prolia if you have low levels of calcium in your blood.
Your doctor may do a blood test to check your calcium levels before you use Prolia.
Do not use Prolia if you are pregnant or trying to get pregnant.
Prolia may harm your unborn baby.
Do not breast-feed while you are having treatment with Prolia.
It is not known if the active ingredient, denosumab, passes into breast milk.
Do not use it in a child or adolescent.
There is no experience with its use in children or adolescents aged 18 years or less.
Do not use it after the expiry date [Exp.] printed on the pack.
If you use it after the expiry date has passed, it may not work as well.
Do not use it if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
Do not use it if the Prolia solution is cloudy or discoloured.
There may be some translucent to white particles of protein in the solution, however the medicine can still be used.
If you are not sure whether you should be given this medicine, talk to your doctor.
Before you are given it
Tell your doctor if:
you have allergies to:
any other medicines
any other substances such as foods, preservatives or dyes.
you have allergy to latex.
The needle cover on the pre-filled syringe contains derivative of latex.
you have calcium deficiency or a vitamin D deficiency.
you are unable to take daily calcium or vitamin D supplements.
you have or have had severe kidney problems, kidney failure or have needed dialysis.
These conditions may increase your risk of getting low blood calcium, if you do not take calcium supplements.
you have been told by a doctor or healthcare professional that you have an intolerance to some sugars.
you become pregnant during your Prolia treatment, if you think you may become pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
you are breast-feeding during your Prolia treatment or plan to breast-feed.
It is not known whether the active ingredient, denosumab, passes into breast milk.
you had or have pain in the teeth gums or jaw, swelling or numbness of the jaw or a “heavy jaw feeling” or loosening of a tooth.
A dental condition called jaw osteonecrosis has been rarely reported in patients treated with Prolia. You may need to have dental treatment completed before starting your medicine.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell him/her before you start using Prolia.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
You should not take Prolia with another medicine containing denosumab.
How it is given
Prolia is given as an injection under the skin. This is called a subcutaneous injection.
Your Prolia is supplied in a pre-filled syringe with an automatic needle guard.
Your doctor may decide that it is best for you or a carer to inject Prolia. Your doctor, nurse or pharmacist will show you or your carer how to use Prolia. Do not use Prolia unless proper training has been given.
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor, nurse or pharmacist carefully.
They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
Instructions for injecting Prolia when supplied in a pre-filled syringe with an automatic needle guard
This section contains information on how you, or the person injecting you (your carer), must use the Prolia pre-filled syringe.
To reduce the risk of accidental injury by the needle, each pre-filled syringe is equipped with an automatic needle guard that is automatically activated to cover the needle after complete delivery of the pre-filled syringe contents.
Guide to parts
Before use After Use
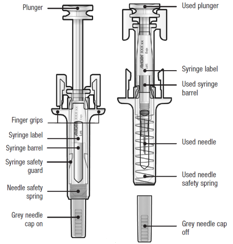
Important
Before you or your carer use Prolia pre-filled syringe with automatic needle guard, read this important information:
It is important that you do not try to give the injection unless training from your doctor, nurse or pharmacist has been received.
Prolia is given as an injection into the tissue just under the skin (subcutaneous injection).
Tell your doctor if you have an allergy to latex (the needle cap on the pre-filled syringe contains a derivative of latex).
DO NOT remove the grey needle cap from the pre-filled syringe until you are ready to inject.
DO NOT use the pre-filled syringe if it has been dropped on a hard surface. Use a new pre-filled syringe and call your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
DO NOT attempt to activate the pre-filled syringe prior to injection.
DO NOT attempt to remove the clear pre-filled syringe safety guard from the pre-filled syringe.
Call your doctor, nurse or pharmacist if you have any questions.
Step 1: Prepare
A: Remove the pre-filled syringe tray from the package and gather the supplies needed for your injection: alcohol wipes, a cotton ball or gauze pad, a plaster and a sharps disposal container (not included).
For a more comfortable injection, leave the pre-filled syringe at room temperature for about 30 minutes before injecting. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
On a clean, well-lit work surface, place the new pre-filled syringe and the other supplies.
DO NOT try to warm the syringe by using a heat source such as hot water or microwave.
DO NOT leave the pre-filled syringe exposed to direct sunlight.
DO NOT shake the pre-filled syringe.
Keep pre-filled syringes out of the sight and reach of children
B: Open the tray, peeling away the cover. Grab the pre-filled syringe safety guard to remove the pre-filled syringe from the tray.

For safety reasons:
DO NOT grasp the plunger.
DO NOT grasp the grey needle cap.
C: Inspect the medicine and pre-filled syringe

DO NOT use the pre-filled syringe if:
the medicine is cloudy or there are particles in it. It must be a clear, colourless to slightly yellow solution.
any part appears cracked or broken.
the grey needle cap is missing or not securely attached.
the expiry date printed on the label has passed the last day of the month shown.
In all cases, call your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Step 2: Get ready
A: Wash your hands thoroughly. Prepare and clean your injection site.

You can use:
Upper part of your thigh.
Belly, except for a 5 cm (2-inch) area right around your belly button.
Outer area of upper arm (only if someone else is giving you the injection).
Clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe. Let the skin dry.
DO NOT touch the injection site before injecting.
DO NOT inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard. Avoid injecting into areas with scars or stretch marks.
B: Carefully pull the grey needle cap straight out and away from your body.
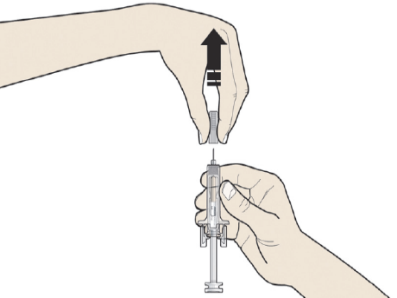
C: Pinch the injection site to create a firm surface.

It is important to keep the skin pinched when injecting.
Step 3: Inject
A: Hold the pinch. INSERT the needle into skin.
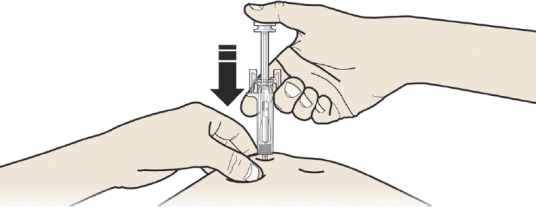
DO NOT touch the cleaned area of the skin.
B: PUSH the plunger with slow and constant pressure until you feel or hear a “snap”. Push all the way down through the snap.
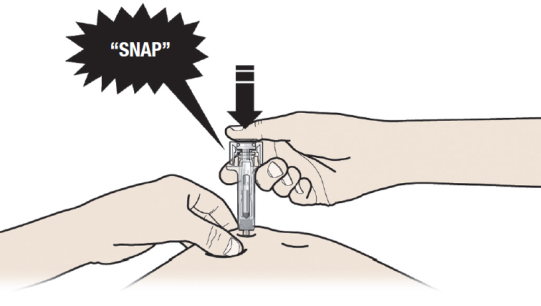
It is important to push down through the “snap” to deliver your full dose.
C: RELEASE your thumb. Then LIFT the syringe off skin.
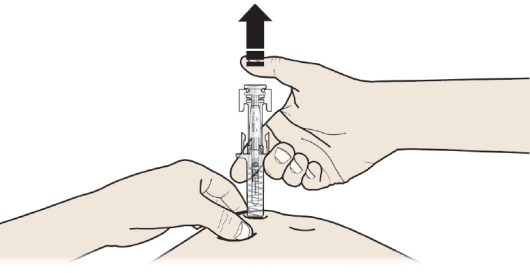
After releasing the plunger, the pre-filled syringe safety guard will safely cover the injection needle.
DO NOT put the grey needle cap back on used pre-filled syringes.
Step 4: Finish
A: Discard the used pre-filled syringe and other supplies in a sharps disposal container.

Medicines should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
Keep the syringe and sharps disposal container out of sight and reach of children.
DO NOT reuse the pre-filled syringe.
DO NOT recycle pre-filled syringes or throw them into household waste.
B: Examine the injection site
If there is blood, press a cotton ball or gauze pad on your injection site. DO NOT rub the injection site. Apply a plaster if needed.
While you are using it
How much is given
The usual dose is 60 mg administered once every 6 months.
You should also take calcium and vitamin D supplements while receiving Prolia. Your doctor, nurse or pharmacist will discuss this with you.
When to use it
Prolia is injected once every 6 months.
Each pack of Prolia contains a reminder card with stickers that can be removed from the carton. Use the peel-off stickers to mark the next injection date on your personal calendar and/or the reminder card to keep a record of the next injection date.

How long to use it
Continue using your medicine for as long as your doctor tells you.
Prolia can treat osteoporosis and bone loss only for as long as you keep having treatment. Please talk to your doctor before you consider stopping treatment.
If you miss a dose
If you miss a dose, it should be administered as soon as possible.
From then on, it should be scheduled every 6 months from the date of the last injection.
If you are given too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (telephone 131126) if you think you or anyone else may have had too much Prolia.
Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
Things you must do
Tell any other doctor, nurses and pharmacist who treat you that you are having this medicine.
If you are about to be started on any other medicine, remind your doctor, nurse or pharmacist that you are being treated with Prolia.
Take calcium and vitamin D supplements if your doctor has told you to.
Most people do not get enough calcium and vitamin D in their diet and supplements are needed to help strengthen bones.
If you become pregnant while using this medicine, tell your doctor immediately.
Your doctor can discuss with you the risks of having it while you are pregnant.
Females that are menstruating should ensure they have adequate contraception while taking Prolia.
Attend all of your doctor’s appointments so that your progress can be checked.
Your doctor may recommend you to have some tests, X-rays and/or bone density scans from time to time to make sure the medicine is working.
Tell your doctor and dentist immediately about any dental symptoms including pain or unusual feeling in your teeth or gums, or any dental infections.
A dental condition called jaw osteonecrosis has been rarely reported in patients treated with Prolia.
Things you must not do
Do not use Prolia to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not give your medicine to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not stop using your medicine without checking with your doctor.
Prolia can treat osteoporosis and bone loss only for as long as you keep having treatment. Please talk to your doctor before you consider stopping treatment.
Things to be careful of
Be careful driving or using machinery until you know how it affects you.
Prolia has no known effects on the ability to drive or use machines but, as a general precaution, if you are driving soon after an injection, arrange to have someone else drive.
Practice good dental hygiene. Your routine dental hygiene should include:
Brushing your teeth and tongue after every meal, including the evening
Gentle flossing once a day to remove plaque.
Use a mirror and check your teeth and gums regularly for any changes such as sores or bleeding gums. If you notice any problems, tell your doctor and dentist immediately.
Side effects
Tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well after using Prolia.
All medicines can have some unwanted side effects. Sometimes they are serious but most of the time they are not. Your doctor has weighed the risks of using this medicine against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
Do not be alarmed by this list of possible side effects.
You may not experience any of them.
All medicines can have side effects. You may need medical treatment if you get some of the side effects.
Ask your doctor, nurse or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
If any of the following happen tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital:
shortness of breath
wheezing or difficulty breathing
swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat or other parts of the body
rash, itching or hives on the skin.
These are very serious side effects. If you have them, you may be having a serious allergic reaction to the medicine. You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation. These side effects are rare.
Tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist immediately if you notice any of the following:
numbness or tingling in your fingers, toes or around the mouth
muscle aches or cramps
seizures.
Severe allergic reaction with skin rash, blisters or fever.
These may be serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention. These serious side effects are rare.
Tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist as soon as possible if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
skin infection with swelling and redness, most commonly affecting the lower leg, that feels hot and tender
feeling feverish
itchy, red or dry skin
blurred or cloudy vision
decreased feeling or sensitivity, especially of the skin
back, muscle or bone pain
joint pain, most commonly affecting the hips, knees and spine
aching muscle, muscle tenderness or weakness, not caused by exercise
pain in the extremities, such as hands and feet
high cholesterol levels in the blood
pain in upper abdomen (belly) that may be accompanied by back pain, nausea, vomiting, fever and/or sweating
ear pain, discharge from the ear and/or an ear infection. These could be signs of bone damage in the ear.
hair loss
These are uncommon or mild common side effects of the medicine.
Contact your doctor if you experience new or unusual pain in your hip, groin or thigh.
This may be an early indication of a possible fracture of the thigh bone. This side effect is very rare.
Contact your doctor if you notice any purple or brownish-red spots, hives or skin sores.
This may be an allergic reaction that can damage blood vessels mainly in the skin. This side effect is very rare.
Tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist if you notice anything that is making you feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some people.
Contact your doctor if you plan to stop taking Prolia.
After your treatment with Prolia is stopped, it is possible that broken bones in your spine may occur especially if you have a history of broken bones in the spine. If your Prolia treatment is stopped, discuss other available treatment options with your doctor.
After using it
Storage
If you need to store your Prolia before use:
Keep your medicine in the refrigerator, between 2°C and 8°C. Do not freeze.
Keep your medicine in the carton in order to protect it from light. If you remove the medicine from the carton it will not keep well.
Your medicine may be left outside the refrigerator to reach room temperature (up to 25°C) before injection. This will make the injection more comfortable.
Once your medicine has been left to reach room temperature (up to 25°C), it must be used within 30 days.
Do not shake or vigorously agitate the pre-filled syringe.
Keep it where children cannot reach it.
Prolia is for single-use in one patient only. Dispose of any unused or expired medicine as instructed below.
Disposal
Return any unused or expired medicine to your pharmacist.
Product description
What it looks like
Your Prolia is supplied in a pre-filled syringe with an automatic needle guard.
Prolia comes in a single pack size containing 60 mg of denosumab in a volume of 1.0 mL (60 mg/1.0 mL).
Each pack contains:
one reminder card with stickers and
one ready to use pre-filled syringe with an automatic needle guard.
Ingredients
Active ingredient: denosumab.
Inactive ingredients within the pre-filled syringe with an automatic needle guard:
acetate
sodium hydroxide
sorbitol
Polysorbate 20
Water for Injection.
This medicine does not contain gluten, tartrazine or any other azo dyes.
Sponsor
Prolia is supplied in Australia by:
Amgen Australia Pty Ltd
(ABN 31 051 057 428)
Level 7, 123 Epping Road
North Ryde NSW 2113
Medical Information: 1800 646 998
This CMI was prepared in September 2020.
Australian Registration Number:
60 mg/1.0 mL pre-filled syringe with an automatic needle guard:
AUST R 159323
Prolia is a registered trademark of Amgen.
Source: Read Full Article