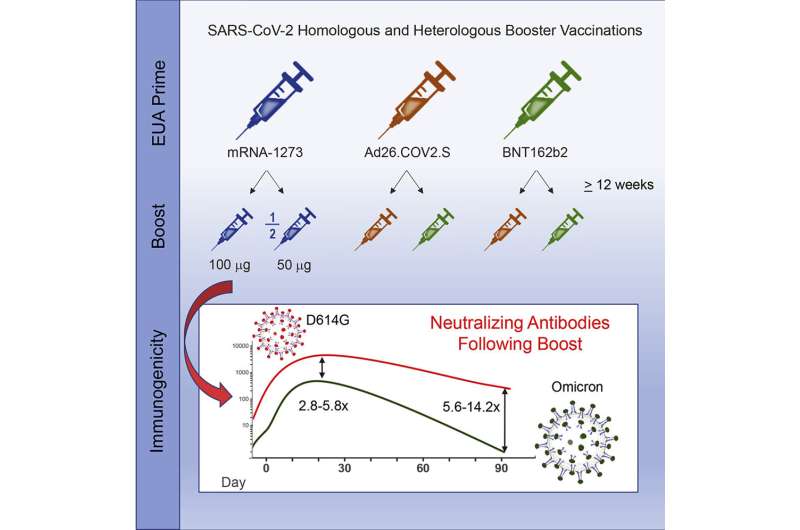
Although COVID-19 booster vaccinations in adults elicit high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, antibody levels decrease substantially within 3 months, according to new clinical trial data. The findings, published today in Cell Reports Medicine, are from a study sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. The trial was led by NIAID’s Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Consortium.
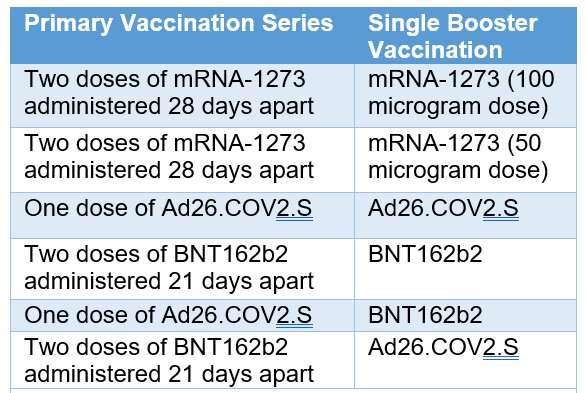
As part of a “mix and match” clinical trial, investigators administered COVID-19 booster vaccines to adults in the United States who had previously received a primary COVID-19 vaccination series under Emergency Use Authorization. Some participants received the same vaccine as their primary series, and others received a different vaccine. Investigators then evaluated immune responses over time. Results previously reported in The New England Journal of Medicine showed all combinations of primary and booster vaccines resulted in increased neutralizing antibody levels in the recipients.
In the new analysis, investigators report that nearly all vaccine combinations evaluated elicited high levels of neutralizing antibodies to the omicron BA.1 sub-lineage. However, antibody levels against omicron were low in the group that received Ad26.COV2.S as both a primary vaccine and boost. Moreover, immune responses to omicron in all groups waned substantially, with neutralizing antibody levels decreasing 2.4- to 5.3-fold by three months post-boost.
Omicron sub-lineages BA.2.12.1 and BA.4/BA.5 were 1.5 and 2.5 times less susceptible to neutralization, respectively, compared to the BA.1 sub-lineage, and 7.5 and 12.4 times less susceptible relative to the ancestral D614G strain. BA.5 currently is the dominant variant in the U.S.
Source: Read Full Article