Physician assistants (PAs) entered dermatology at a higher rate than all other specialties combined from 2013 to 2018, based on national certification data.
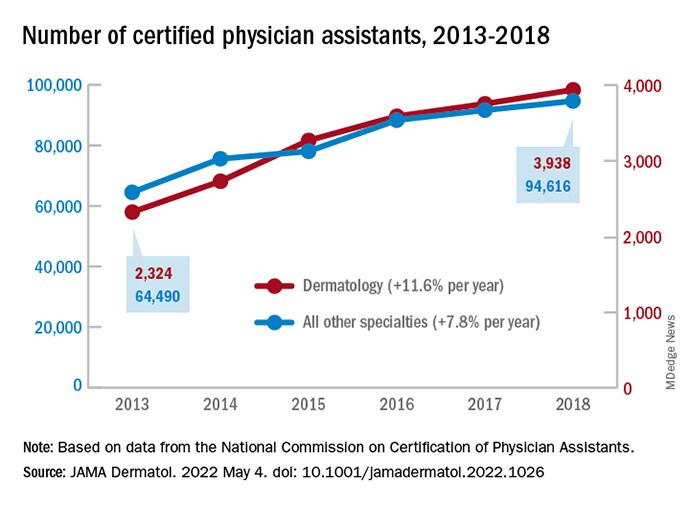
Dermatology added PAs at a mean rate of 11.6% annually over that 6-year period, compared with a mean of 7.8% for all other specialties (P <.001), as the National Commission on Certification of Physician Assistants (NCCPA) tallied 2,324 working in dermatology and 64,490 in all other specialties in 2013 and 3,938/94,616, respectively, in 2018, Justin D. Arnold, MD, of the University of California, Irvine, and associates reported in JAMA Dermatology.
“There is, however, a lack of racial and ethnic diversity within the dermatology PA workforce,” they noted. A detailed comparison using the 2018 data showed that only 1.6% of dermatology PAs identified as Black, compared with 3.7% of those in all other specialties (P <.001), although “similar rates of Hispanic ethnicity were observed” in dermatology PAs (6.0%) and PAs in other fields (6.5%), the investigators added.
That was not the case for women in the profession, as 82% of PAs in dermatology were female in 2018, compared with 67% in the other specialties. Dermatology PAs also were significantly more likely to work in office-based practices than their nondermatology peers (93% vs. 37%, P < .001) and to reside in metropolitan areas (95% vs. 92%, P < .001), Dr. Arnold and associates said in the research letter.
The dermatology PAs also were more likely to work part time (30 or fewer hours per week) than those outside dermatology, 19.1% vs. 12.9% (P < .001). Despite that, the dermatology PAs reported seeing more patients per week (a mean of 119) than those in all of the other specialties (a mean of 71), the investigators said.
The total number of certified PAs was over 131,000 in 2018, but about 25% had not selected a principal specialty in their PA Professional Profiles and were not included in the study, they explained.
“Although this study did not assess the reasons for the substantial increase of dermatology PAs, numerous factors, such as a potential physician shortage or the expansion of private equity–owned practices, may contribute to the accelerating use of PAs within the field,” they wrote.
This article originally appeared on MDedge.com, part of the Medscape Professional Network.
Source: Read Full Article