Editor’s note: Find the latest COVID-19 news and guidance in Medscape’s Coronavirus Resource Center.
The proportion of children aged 12-15 years who have completed their COVID-19 vaccine regimen jumped by over 50% in just 1 week, but there has been a slowdown in first vaccinations, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
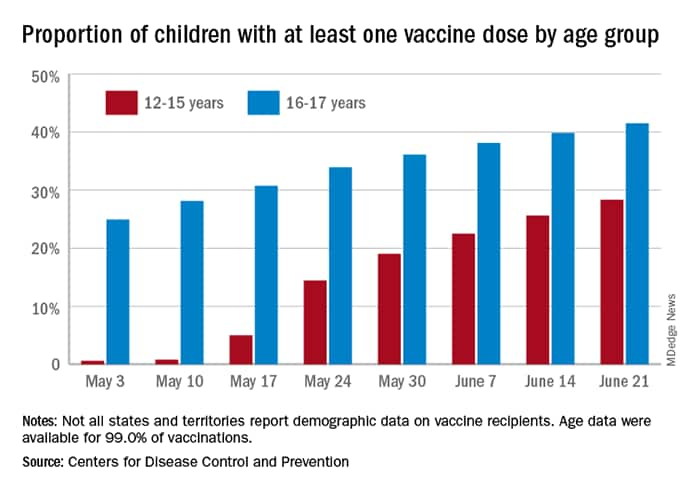
As more adolescents became eligible for a second dose of the Pfizer vaccine since it received approval from the Food and Drug Administration in mid-May, the share of 12- to 15-year-olds considered fully vaccinated rose from 11.4% on June 14 to 17.8% on June 28, an increase of 56%, the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker indicated June 22
For children aged 16-17 years, who have been receiving the vaccine since early April, full vaccination rose by 9.6% in that same week, going from 29.1% on June 14 to 31.9% on June 21. The cumulative numbers for first vaccinations are higher, of course, but are rising more slowly in both age groups: 41.5% of those aged 16-17 had received at least one dose by June 21 (up by 4.3%), with the 12- to 15-year-olds at 28.3% (up by 10.5%), based on the CDC data.
Limiting the time frame to just the last 2 weeks, however, shows the opposite of rising among the younger children. During the 2 weeks ending June 7, 17.9% of those initiating a first dose were 12-15 years old, but that 2-week figure slipped to 17.1% as of June 14 and was down to 16.0% on June 21. The older group was slow but steady over that time: 4.8%, 4.7%, and 4.8%, the CDC said. To give those figures some context, those aged 25-39 years represented 23.7% of past-2-week initiations on June 7 and 24.3% on June 21.
Although no COVID-19 vaccine has been approved for children under 12 years, about 0.4% of that age group – just over 167,000 children – have received a first dose and almost 91,000 are fully vaccinated, according to CDC data.
This article originally appeared on MDedge.com, part of the Medscape Professional Network.
Source: Read Full Article